Products
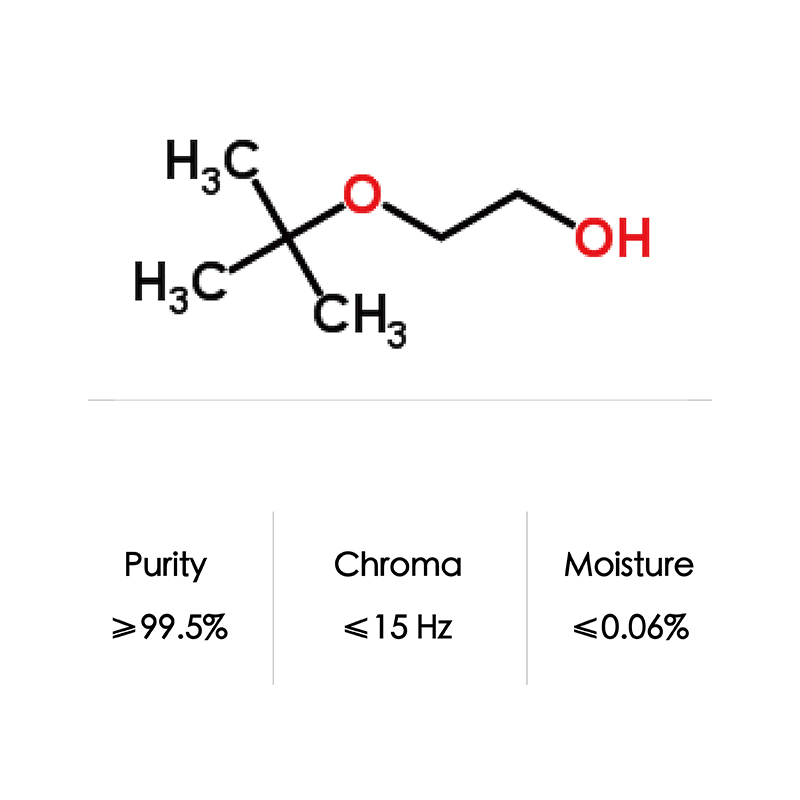
CAS No. 7580-85-0 Ethylene Glycol Mono-Tert-Butyl Ether/Etb/Ethylene Glycol Tertiary Butyl Ether
Product Description
2-Butoxyethanol is a solvent for paints and surface coatings, as well as cleaning products and inks. Products that contain 2-butoxyethanol include acrylic resin formulations, asphalt release agents, firefighting foam, leather protectors, oil spill dispersants, degreaser applications, photographic strip solutions, whiteboard and glass cleaners, liquid soaps, cosmetics, dry cleaning solutions, lacquers, varnishes, herbicides, latex paints, enamels, printing paste, and varnish removers, and silicone caulk. Products containing this compound are commonly found at construction sites, automobile repair shops, print shops, and facilities that produce sterilizing and cleaning products.
Properties
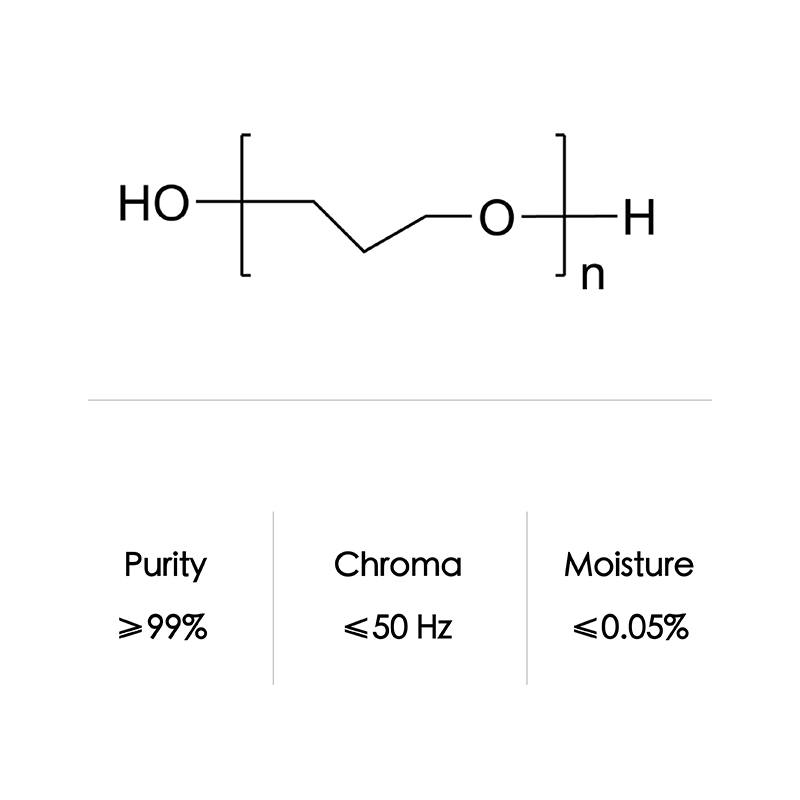
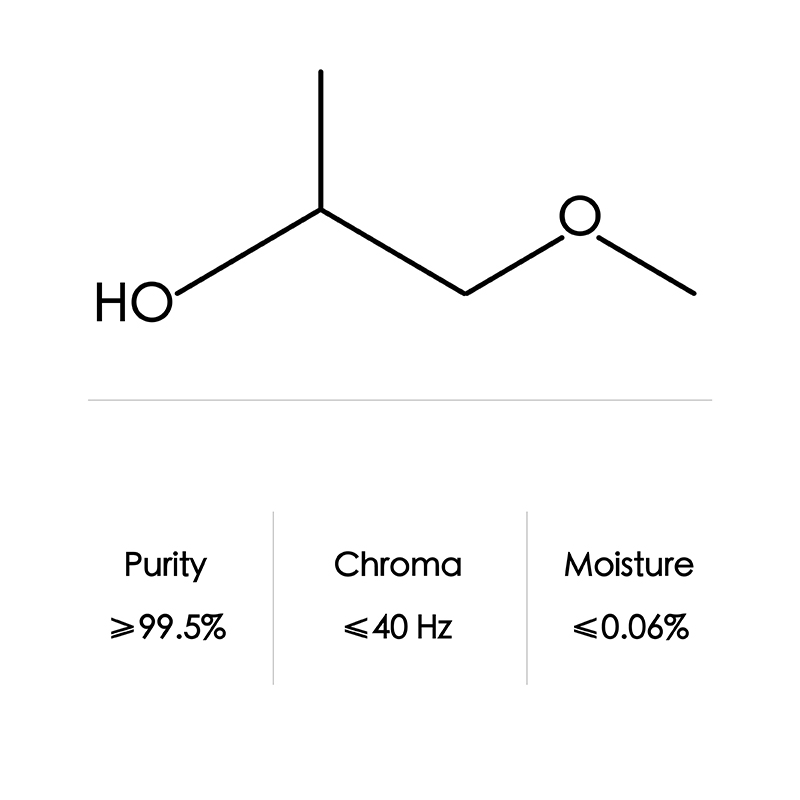
| Formula | C6H14O2 | |
| CAS NO | 7580-85-0 | |
| appearance | colorless, transparent, viscous liquid | |
| density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 | |
| boiling point | 144.0±8.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| flash(ing) point | 47.3±7.7 °C | |
| packaging | drum/ISO Tank | |
| Storage | Store in a cool, ventilated, dry place, isolated from the fire source, loading and unloading transportation should be stored in accordance with the provisions of flammable toxic chemicals | |
*The parameters are for reference only. For details, refer to COA
Application
| High boiling point solvents for paints, fiber wetting agents, plasticizers, intermediates for organic synthesis. |
Storage Precautions
2-Butoxyethanol is commonly produced for the oil industry because of its surfactant properties.
In the petroleum industry, 2-butoxyethanol is a component of fracturing fluids, drilling stabilizers, and oil slick dispersants for both water-based and oil-based hydraulic fracturing.[clarification needed] When liquid is pumped into the well, the fracturing fluids are pumped under extreme pressure, so 2-butoxyethanol is used to stabilize them by lowering the surface tension.As a surfactant, 2-butoxyethanol absorbs at the oil-water interface of the fracture.The compound is also used to facilitate the release of the gas by preventing congealing.It is also used as a crude oil–water coupling solvent for more general oil well workovers.
2-Butoxyethanol most commonly enters the human body system through dermal absorption, inhalation, or oral consumption of the chemical.The ACGIH threshold limit value (TLV) for worker exposure is 20 ppm, which is well above the odor detection threshold of 0.4 ppm. Blood or urine concentrations of 2-butoxyethanol or the metabolite 2-butoxyacetic acid may be measured using chromatographic techniques. A biological exposure index of 200 mg 2-butoxyacetic acid per g creatinine has been established in an end-of-shift urine specimen for U.S. employees.2-Butoxyethanol and its metabolites fall to undetectable levels in urine after about 30 hours in men.
Advantage
Product quality, sufficient quantity, effective delivery, high quality of service It has an advantage over a similar amine, ethanolamine, in that a higher concentration may be used for the same corrosion potential. This allows refiners to scrub hydrogen sulfide at a lower circulating amine rate with less overall energy usage.